Appendix C
Internet Program settings
This chapter will review the security settings of today’s two most popular Internet browsers. To prevent the installation of malware on your computer, to erase temporary files – the result of your browsing activity - and to offer you the best possible protection against other Internet insecurities, it is important to make sure that your Internet browsing program is configured correctly .
The are several precautions you should take when using any Internet-browsing program. The main point is never to visit a website ‘just for the sake of it’. The Internet, like a dark alley in a strange neighbourhood, has become an insecure place to browse. If you are on your work computer, only go to the sites you absolutely have to visit.
Do not install any programs that make it easier for you to fill out web forms and to save your passwords or offer other seemingly useful features. Most of these programs come with a bunch of spyware, advertising and other malicious code in hand. Never ask your browser to remember a password for you – use a password program (Digital Security Toolkit
). In short, do not try to make your web browsing easier by installing additional software.
Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (IE) has a reputation of being the least secure out of all Internet browsing programs. If you are using Microsoft Windows, you have Internet Explorer already installed. It is very difficult and often impossible to uninstall this program from your computer. Your can either strengthen the security of IE or install a parallel browsing program.
Always make sure you are using the latest version of IE and have installed all the necessary updates provided by Microsoft. On the menu bar select:
Tools > Windows Update
Let Windows check your computer and present a list of necessary updates. Alternatively, you can go to www.microsoft.com/windows/ie/ie6/downloads and choose to download IE6 in the desired language manually.
Basic Security Settings
IE can be a reliable and secure browser, if you specify to it which websites you trust and which you do not. By default we should ask it to NOT trust any websites unless we allow it to do so.
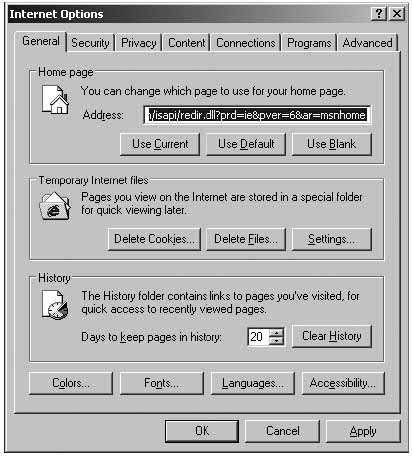
Tools > Internet Options
Go to “Security” tab and move the security level bar on this “Internet zone” to “High”. If you can’t see the security level bar, click “Default level” and move it to “High”. This will protect you from many dangers, like, for example, harmful Active-X content
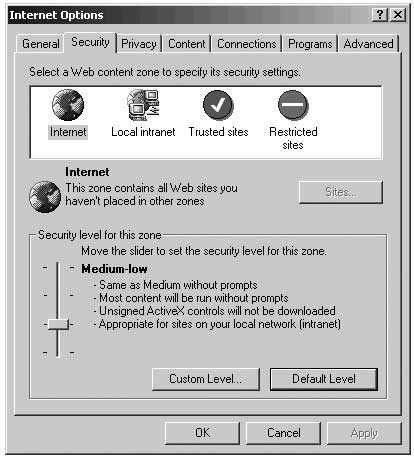
Internet Explorer options
Click “Trusted Sites” and move the security level bar to “medium low”.
If you can’t see the security level bar, click “Default level” and move
it to “Medium low”. You must add sites you absolutely trust to your
“Trusted Sites” by pressing the “Sites” button. Add pages like
*.microsoft.com, *.bbc.co.uk, *.frontlinedefenders.org, any webmail you
use and other websites you regularly visit and trust. Press “Add”. Now,
all the pages belonging to Microsoft (like
http://windowsupdate.microsoft.com, for example) are considered trusted.
The * denotes that all web pages within this domain are treated as such.
Also, remember to disable “Require server verification (https) for all
sites in this zone”! The sites you add will be able to function to their
full capacity and will not be restricted by any security limitations, so
that cookies, JavaScript, Active-X, etc. will work in these pages. Press
OK to go back to the rest of the settings.
Next, click ‘other zones’ and change security preferences on them to ‘High’. This will ensure that all zones other than ‘Trusted Sites’ zone are as secure as possible. Note that from now on the sites that are not listed in the ‘Trusted Sites’ category will be limited in their function on your PC. Some may not even load. This may be frustrating at first, but is an excellent way to secure your Internet browsing experience with IE.
Go to the next page, called ‘Privacy’, and move the bar to the top. This makes sure no cookies from Internet sites are stored on your computer. The pages you have added to your ‘Trusted Sites’ will still be able to download cookies.
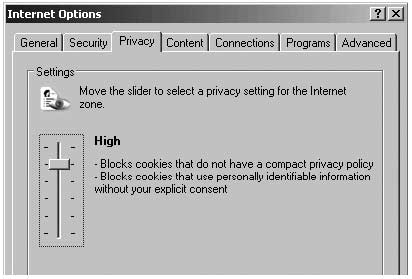
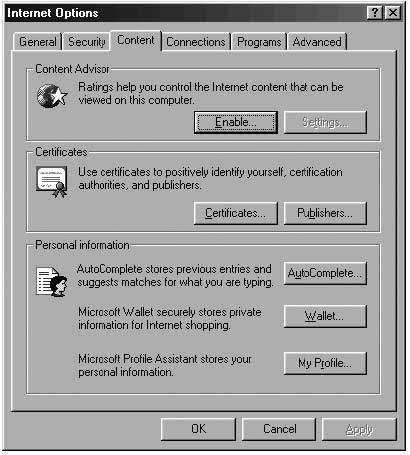
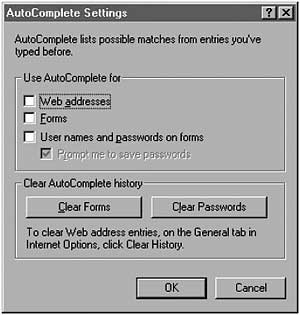
Go to the next page, called “Content”, and in it - go to “Autocomplete”.
Disable all marks. This makes sure that no passwords or forms are saved
to the browser that someone might use for malicious purposes. Passwords
are meant to be memorised or kept in a password program (see ‘Passwords’
chapter), not written down anywhere! Also, remember to clear both the
passwords and the forms fields. Press OK to go back to rest of the
settings.
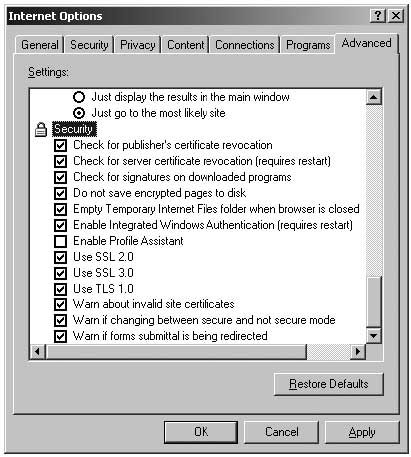
Go to the “Advanced” page and make sure you have the following enabled:
- Automaticaly check for Internet Explorer updates”
- Use SSL 3
- Use TLS 1
- Check for signatures on downloaded programs
- Check for publisher’s certificate revocation
- Check for server certificate revocation
- Do not save encrypted pages to disk
- Warn about invalid site certificates
Make sure you have the following disabled:
- Install on demand -other
- Use AutoComplete
- Use third-party browser extensions
- Enable install on demand
- Enable integrated Windows authentication
Deleting Temporary Files
It is good practice to delete the temporary files our Internet browser collects during the working session. This is particularly important when using public computers. Even though these actions will not wipe the temporary data (see ‘Information Backup, Destruction and Recovery’ chapter), they will delete it from immediate access by an outsider. At the end of every session, run the following commands in the IE browser.
Tools > Internet Options
General Page
Click the ‘Delete Cookies’, ‘Delete Files’ & ‘Clear History’ buttons in succession.
Mozilla Firefox
The Firefox web browser, a recent addition to the world browser market, has proved tremendously popular. It is reclaiming the market monopoly from Internet Explorer. Its main advantages are high security settings, built into the browser by default, and the fact that it is written in open code, meaning that anyone with some programming skills can write an additional program to work alongside it (extensions) or improve the browser’s functionality (plug-ins). The majority of existing spyware will not affect your computer, if you browse the Internet through Mozilla Firefox.
Basic Security Settings
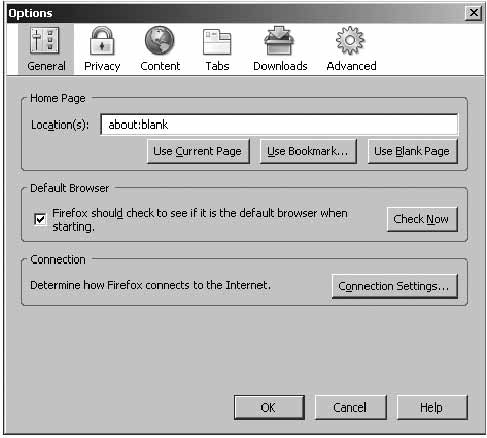
In the Firefox browser go to:
Tools > Internet Options
On the ‘Content’ page, you can specify Firefox to block pop-ups, run Java and Java script. You can leave these settings as they are, by default, or modify them.
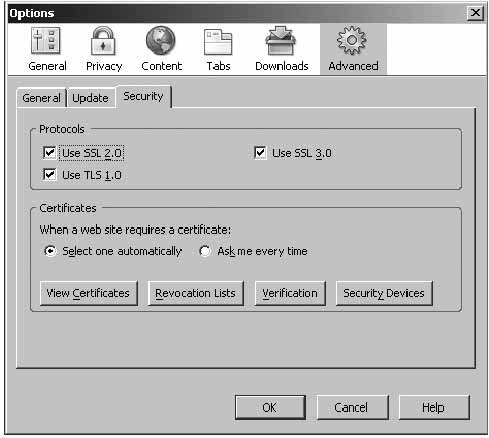
Make sure the ‘Advanced’ page has all options enabled and for certificates – ‘Select one automatically’.
Deleting Temporary Files
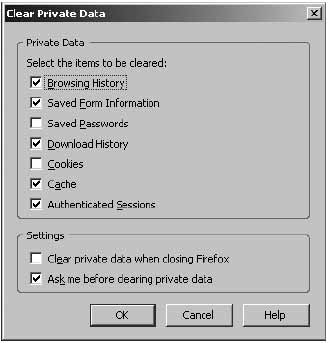
Firefox makes it very easy to delete temporary data from the computer. In the ‘Internet Options’ window, click on the ‘Privacy’ page and the ‘Settings’ button in the bottom right-hand corner.
Enable all functions to be deleted upon exiting the program.
This will be executed automatically when closing the program down. To enable file deletion whilst using the Firefox browser, go to
Tools > Clear Private Data
Press OK.
|